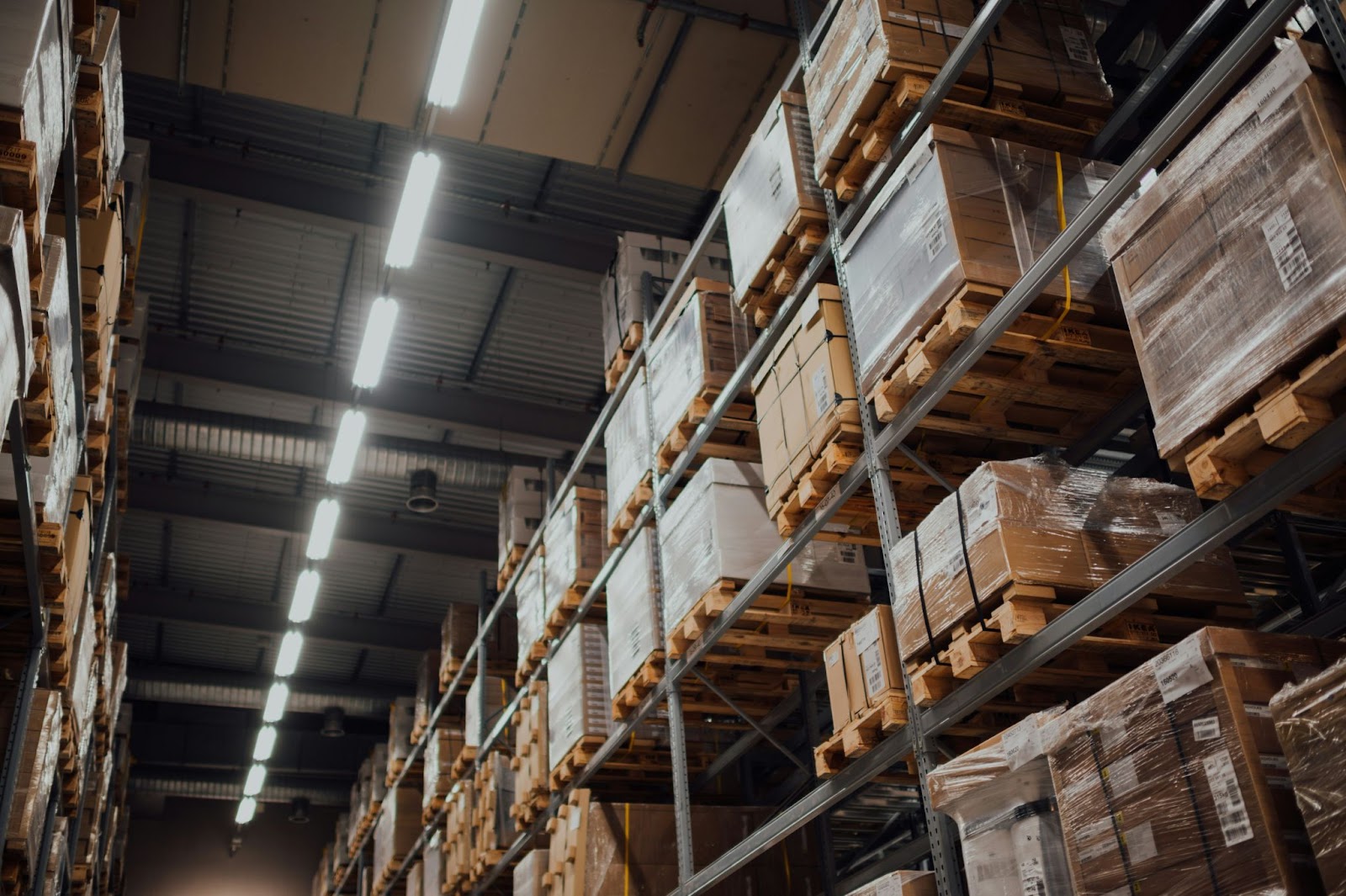
Warehouse types play a crucial role in logistics and supply chain management. They are the epicenters of product storage, handling, and distribution, ensuring that goods reach their intended destinations in a timely and efficient manner. However, not all warehouses are equal.
There are several types of warehouses, each with its unique characteristics, advantages, and drawbacks.
In this comprehensive guide, we will discuss the various types of warehouses, their functions, and how they contribute to the overall efficiency of the supply chain.
Understanding the Role of Warehouses
Before we discuss the different types of warehouse construction, it’s essential to understand the functions of warehouses in the supply chain.
Warehouses serve as storage points for goods and products between the time they are produced and the time they are needed for distribution, also known as the warehousing supply chain.
They are critical in ensuring that goods are available when and where they are needed, thereby preventing potential shortages and disruptions.
Additionally, warehouses provide a controlled environment for goods, protecting them from damage and theft while offering flexibility and space to accommodate seasonal fluctuations
In essence, warehouses are more than just storage facilities; they are vital cogs in the supply chain that enable efficient and effective logistics operations.
Generally, steel maximizes expansion and flexibility through clearspan construction, eliminating the need for internal columns. This approach creates wide-open, adaptable warehouse spaces, allowing for easy reconfiguration as storage needs change.
Learn more about Steel-Constructed Warehouses.
Types of Warehouses
Now that we have a clear understanding of warehouses’ role, let’s explore the different types of warehouses.
- Private warehouses
- Public warehouses
- Bonded warehouses
- Cooperative warehouses, and
- Distribution centers
Private Warehouses
Manufacturers and resellers own and operate private warehouses for their use. They provide complete control over the warehousing operations, including storage, inventory management, and shipping. This control can increase efficiency and cost savings, especially for companies with large volumes of goods or complex logistics needs.
However, private warehouses also come with significant upfront costs, including the cost of land, construction or purchase, and ongoing maintenance.
They also require a substantial investment in warehouse management systems and equipment. Therefore, large corporations with the financial resources to invest in their warehousing facilities typically use private warehouses.
Public Warehouses
Third-party companies, on the other hand, own and operate public warehouses. They offer warehousing services to multiple clients on a contract basis. This means that businesses can rent space in a public warehouse for a specific period, usually on a month-to-month basis.
The main advantage of public warehouses is their flexibility. Businesses can easily scale their warehousing needs up or down based on demand without worrying about the costs and responsibilities of owning and managing a warehouse.
Did You know?
Steel-constructed warehouses are flexible and easy to scale. The modular nature of steel allows seamless extensions for public warehouses that require new sections as demand for storage space grows.
Public warehouses also offer a range of services, including inventory management, packing and shipping, and logistics consulting, making them a convenient option for small to medium-sized businesses.

Bonded Warehouses
Bonded warehouses are a type of public warehouse licensed by the government to store imported goods until customs duties are paid. They are typically located near ports and are used by importers, exporters, and customs agents.
Bonded warehouses offer a secure environment for the storage of goods and services such as packing, repacking, and sorting.
The main advantage of bonded warehouses is that they allow businesses to defer payment of customs duties until the goods are sold or removed from the warehouse. This can significantly improve cash flow, especially for businesses dealing with high-value goods or large volumes of imports.
However, bonded warehouses also come with strict regulations and oversight, which can be a drawback for some businesses.
That’s why many businesses often opt for steel-constructed warehouses as they are typically spacious, with column-free layouts for easy inspection of goods by customs officials. This streamlines inspection processes and reduces delays.
The open space of steel warehouses enables clear zoning for separating bonded and non-bonded goods, which is crucial for customs compliance.
Cooperative Warehouses
A cooperative of businesses owns and operates cooperative warehouses, pooling their resources to share the warehousing costs and benefits.
Small and medium-sized businesses that cannot afford to invest in their own warehouses but need more control and flexibility than public warehouses typically use them.
Cooperative warehouses offer various services, including storage, inventory management, and distribution. A board elected by member companies governs cooperative warehouses.
The main advantage of cooperative warehouses is that they allow businesses to share the costs and risks of warehousing while benefiting from shared resources and expertise.
Distribution Centers
Distribution centers are a type of warehouse that focus on the rapid movement of goods from the warehouse to the end customer. Businesses with high volumes of goods and fast turnaround times, such as e-commerce companies and retailers, typically use them.
Distribution centers are designed for efficiency, with advanced warehouse management systems, automated picking and packing processes, and streamlined shipping operations.
They also often offer value-added services, such as order fulfillment, returns management, and cross-docking, where goods are unloaded from incoming trucks and loaded onto outbound trucks with minimal storage in between.

At Steelco, we provide warehouse construction services that create an ideal environment to capitalize on the full potential of warehouse racking types. This translates to optimized storage capacity, operational efficiency, and flexibility for long-term warehouse success.
Choosing the Right Type of Warehouse
Choosing the right type of warehouse depends on various factors, including the nature of your business, the volume, and type of goods, the need for value-added services, functions, and your budget. It’s important to consider these factors carefully and consult a logistics expert to make an informed decision.
For example, a public warehouse might be the best option if you’re a small business with fluctuating warehousing needs. On the other hand, investing in a private warehouse might be more cost-effective in the long run if you’re a large corporation with high volumes of goods and complex logistics needs. Similarly, a bonded warehouse could offer significant cash flow advantages if you’re an importer or exporter dealing with high-value goods.
In conclusion, understanding warehouses’ different types and functions can help businesses optimize their supply chain operations and make more informed logistics decisions.
Whether it’s a private warehouse, a public warehouse, a bonded warehouse, a cooperative warehouse, or a distribution center, each type of warehouse offers unique advantages that can contribute to the efficiency and effectiveness of your logistics operations.
At SteelCo Buildings, our team of experts with over 20 years of experience can help you make informed decisions when choosing a warehouse type for your business. Contact us.
———————-
Frequently Asked Questions
The two basic types of warehouses are?
- Private Warehouses: Owned and operated by manufacturers, wholesalers, or distributors for their goods and operations. They offer full control over storage and distribution processes.
- Public Warehouses: Third-party facilities that offer storage and logistics services to multiple businesses for a fee. A good option for companies needing flexible storage space, short-term requirements, or specialized services (like cold storage).
What is the purpose of warehousing supply chain and warehousing?
Warehousing supply chains ensure the smooth, cost-effective, and reliable flow of goods from producers to consumers, playing a critical role in modern commerce.
What are the functions of a warehouse?
A warehouse’s primary functions include receiving, storing, and managing inventory to ensure products are available when and where needed. They protect goods from potential damage, offer flexibility in handling fluctuating demand, and can provide value-added services such as labeling, customization, and product assembly to streamline supply chain operations.